Week 3: Python 2 (Teaching notes)
| Time (start) | Duration | Topic | Additional materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| 00:00 | 10 min | Set up the example repository | |
| 00:10 | 60 min | Part 4: Object-oriented code | notebook 2 |
| 01:10 | 30 min | Part 5: Programmatic use of CoLRev | |
| 01:40 | 10 min | Part 6: Save and commit changes | |
| 01:50 | 10 min | Wrap-up | |
| 02:00 | 120 min | Overall |
- Have students start the codespaces on Github from colrev/tutorial branch (see notebook)
- Ask students how they interpret the error messages, articulate the problem, how they would solve the problem, where/how they would search (do not provide solutions)
- Run the pre-commit hooks a few times to illustrate the typing information
It is important to run colrev in a separate data directory.
Clearly demonstrate to students how to set both up in explorer and bash.
Setup for the data directory (code: see setup in notebook)
# generally: in shell:
cd .. && mkdir data
code -a /workspace/data
# or: Datei: Ordner zum Arbeitsbereich hinzufügen (select workspace/data)
# open two separate shells
Also show the history of the example colrev project.
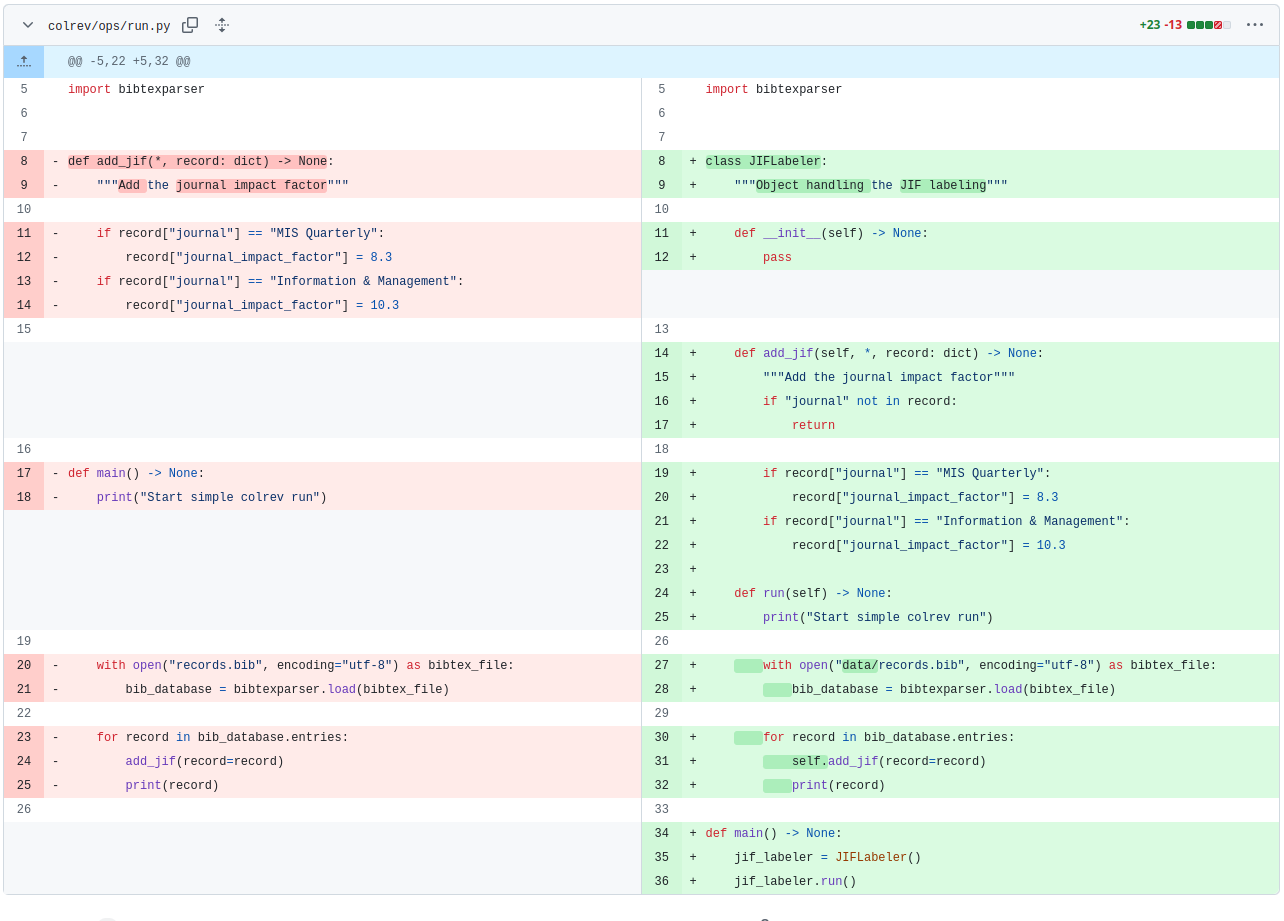
Object-oriented programming
- Encourage students to program using objects (instead of procedurally)
- Show simple object syntax
class Dog: # Define a class
# Constructor method
def __init__(self, name, age):
self.name = name # instance variable
self.age = age
def bark(self): # Instance method
print(f"{self.name} says woof!")
def birthday(self):
self.age += 1
print(f"{self.name} is now {self.age} years old!")
# Create objects (instances) of the class
dog1 = Dog("Buddy", 3)
dog2 = Dog("Luna", 5)
# Call methods on the objects
dog1.bark() # Output: Buddy says woof!
dog2.birthday() # Output: Luna is now 6 years old!
- Notice: when creating the
run()method, the jif_labeler_instance switches to “self”.
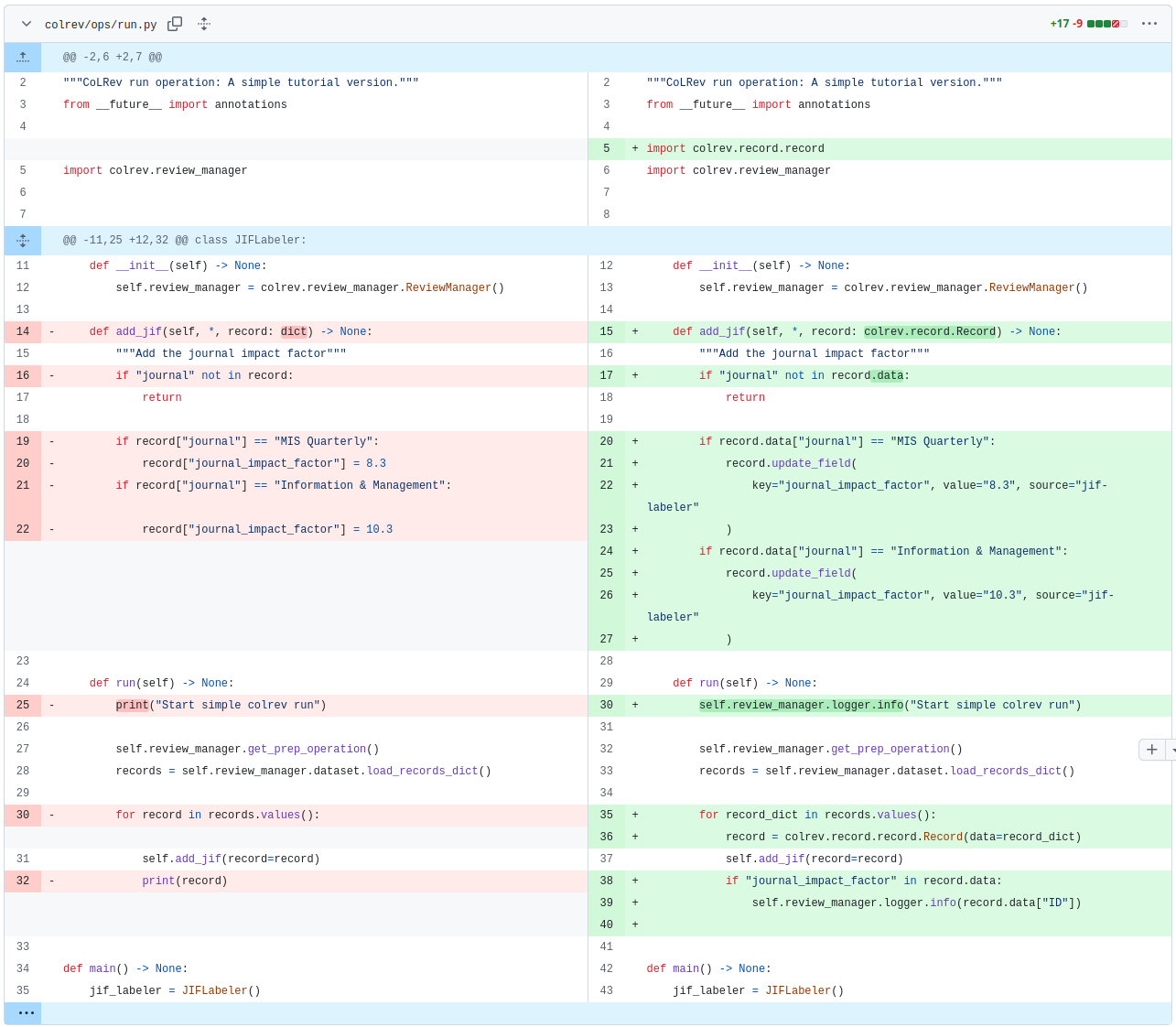
Using CoLRev infrastructure
- Go to API reference
- Navigate through the classes / dataset

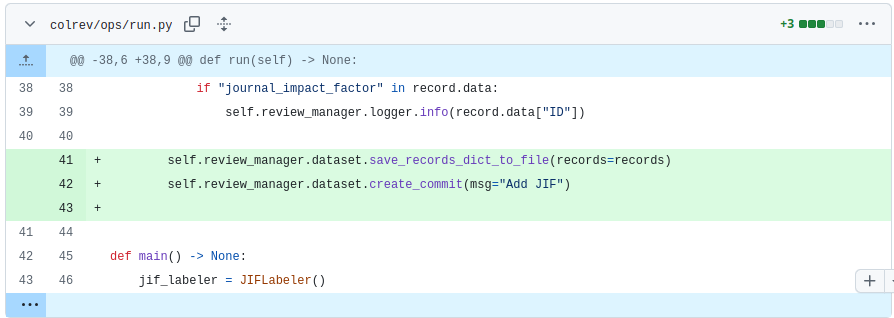
Save and commit
- Ask students to analyze the changes that were actually committed
- Remind students that this is something they should have seen in the CoLRev tutorial.
Merging Exercise (moved to a later time point)
Until the 10th of November
- explain to the students what the merging exercise is about
- tell them about the survey and that it is important to fill it out for the best practice session
- maybe create even a slide for students to look it up again
Wrap-up
Deliverables
- The merge should be done in one of the first hacking session meetings
- Students should prepare the merge by selecting suitable branches and explaining why they should be merged
- We will complete the merge together with the students to prevent and solve problems
Note: “synchronizing with upstream” would be one example of a merge.
Next: Best practice and hacking sessions (per group)
- Suggest pair-programming
- Which CoLRev-objects or libraries will be needed, and which steps are required
- Create a fork for the team, give access to team members, and add a note to the issue feed
- Check the resources provided with the issue, discuss the project, and make plans
Resources
- Python programming for data science with Python basics (and unit tests)
- Welcome to Python Packages