Python session 2
-blue)
We your feedback and suggestions on this notebook!
With this notebook, you can refactor to object-oriented code, switch to a real colrev project, load the records using the colrev classes, and save changes to create a commit.
- Learn how to write object-oriented code
- Learn how to use
colrevinfrastructure- Learn how to save and commit changes
📑 Session slides: ➡️ View online · ⬇️ Download PDF
| Part | Label | Time (min) |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | 10 | |
| Part 1 | Object-oriented programming | 30 |
| Part 2 | Programmatic use of colrev | 40 |
| Part 3 | Save and commit changes | 30 |
| Wrap-up | 10 | |
| Overall | 120 |
Continue working on your codespace started in the previous session.
Resume the codespace as follows:
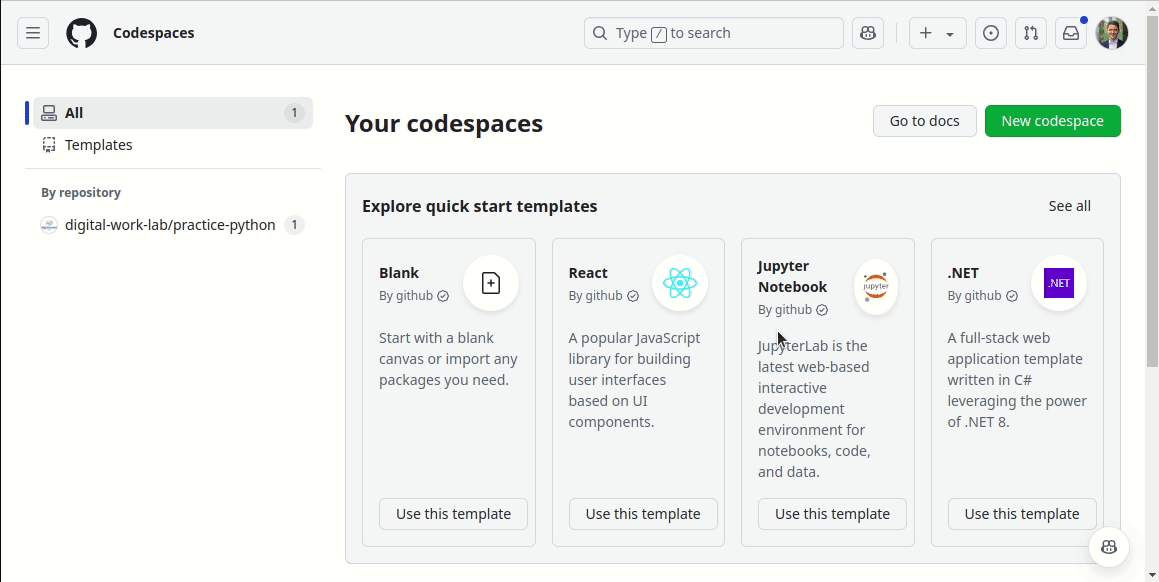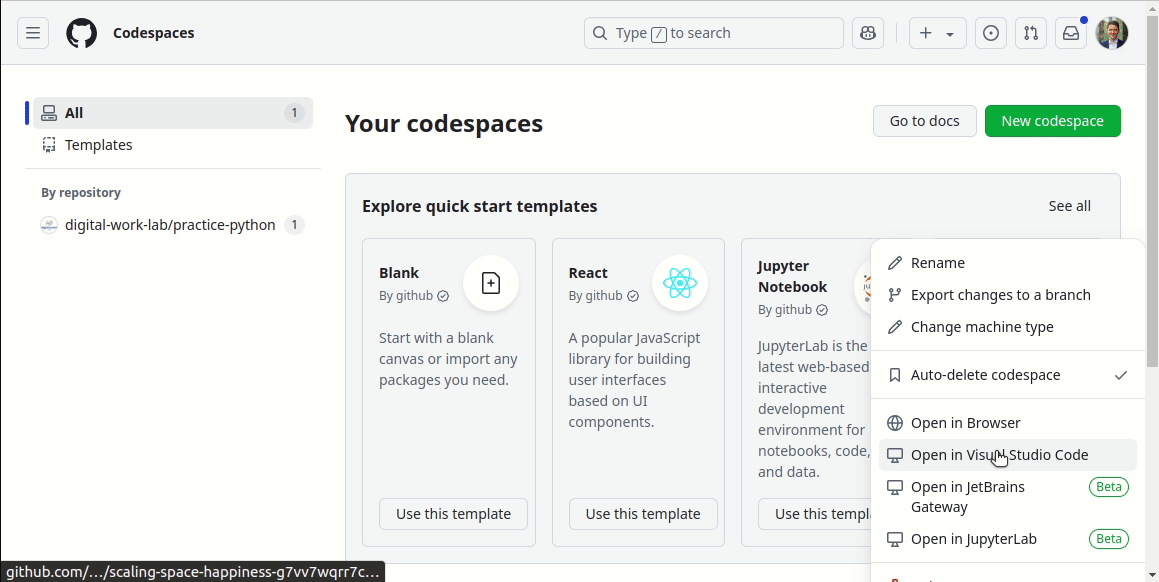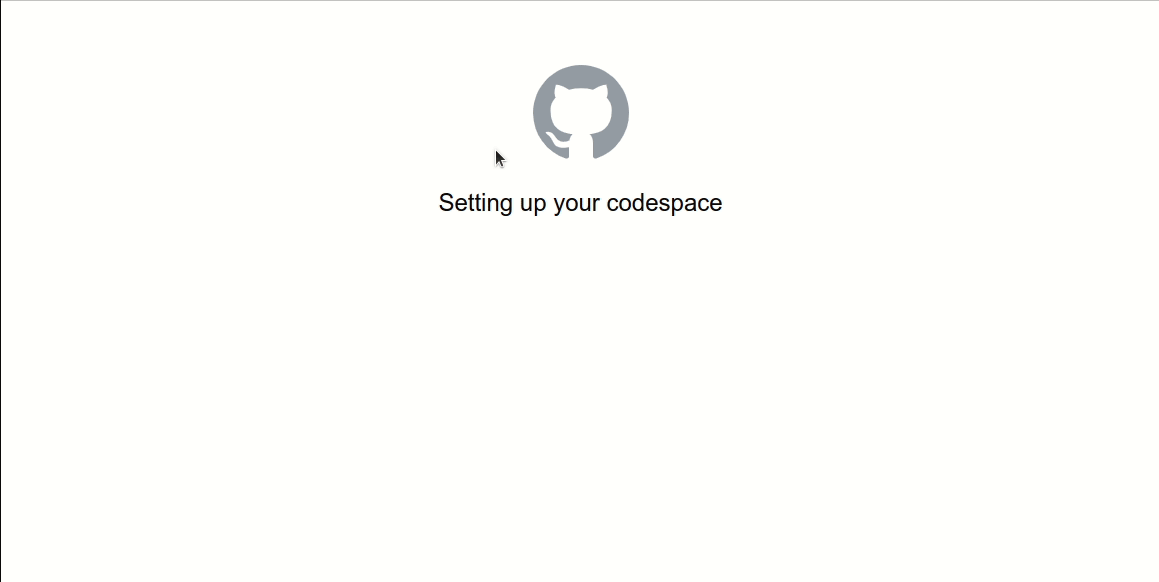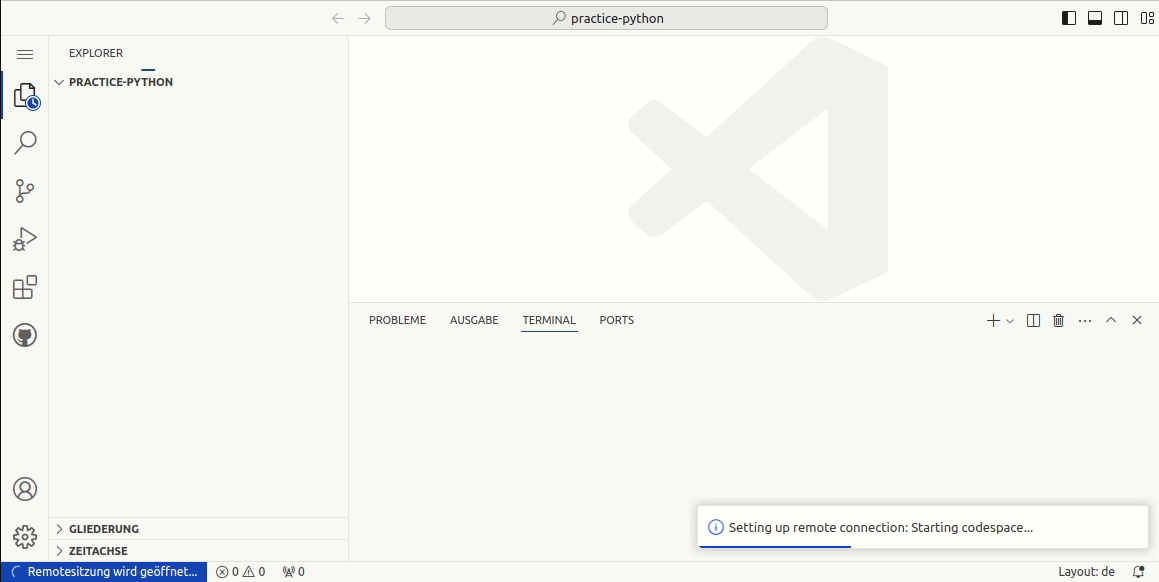
To select the starting point (commit), run:
git reset --hard f859208f8ddaf5651f5c2b378e7e07543ca7cdd1
Part 1. Object-oriented code
Object-oriented programming
Our next goal is to implement the previous example (adding the journal impact factor to the records) using Python objects and methods, and using the colrev infrastructure.
Task: Create the JIFLabeler class, instantiate an object, and add the add_jif() method (based on the Python objects/methods syntax). Run and revise the code (if necessary).
Hint: Also adapt the path of the records to data/records.bib. This is where colrev projects store the main records file.
To select the solution, run:
git reset --hard 670c56408684f8b3b466c22f25a62fe2bed88bd1
Part 2: Programmatic use of colrev
Using colrev infrastructure
In the following, we start to work with the colrev library. To install it, run:
uv install colrev
To use the colrev infrastructure, take a look at the API reference and find the classes and methods that can be used to load and save records.
Task: Rewrite the code in run.py to use colrev classes and methods. When instantiating the JIFLabeler, instantiate a ReviewManager object and keep it as an object variable. When calling the main method, the records should be loaded by using the ReviewManager’s dataset methods.
Hint: Remember to import the required modules. Test your code, run the linters, and try to address potential warnings.
To select the solution, run:
git reset --hard 29e5cf28e3c96940e19e5af470977092ef3b8d47
Optional challenge
To improve the code, try to implement these two changes:
- Instead of using
print()statements, use theReviewManager’s logger. - Instead of using the record dicts, work with the
Recordclass and itsupdate_field()method.
To select the solution, run:
git reset --hard 8a4d064771f2b527b6479ac967bde0a5aabd9b19
Part 3: Save and commit
Save and commit changes
Task: Save the records (using the dataset attribute of ReviewManager) and create a commit (using the ReviewManager).
Review the commit and its content.
To select the solution, run:
git reset --hard 99f4477aabd4dfd5eaec7ddefefab2b632ef95e0
Wrap-up
🎉🎈 You have completed the Python commit notebook – good work! 🎈🎉
In this notebook, we have learned to:
- Write object-oriented code in Python
- Use
colrevprogrammatically - Save and commit changes in a
colrevproject - Use stop and resume in GitHub Codespaces
Delete your codespace Remember to delete your codespace after the session.
